Sex related differences in the effect of cognitive behavioral therapy on emotional arousal and salience circuits and the role of the gut microbiome
Overall Goal
To identify sex differences in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) responders, in the response of the emotional arousal and salience brain networks and in gut microbiome parameters, and to examine clinical characteristics that are associated with these responses. This study will be the first of its kind to directly study sex differences in BGM pathways in relationship to a clinically effective IBS treatment. It will provide unique data regarding mechanism of action for a centrally targeted IBS treatment.
Background
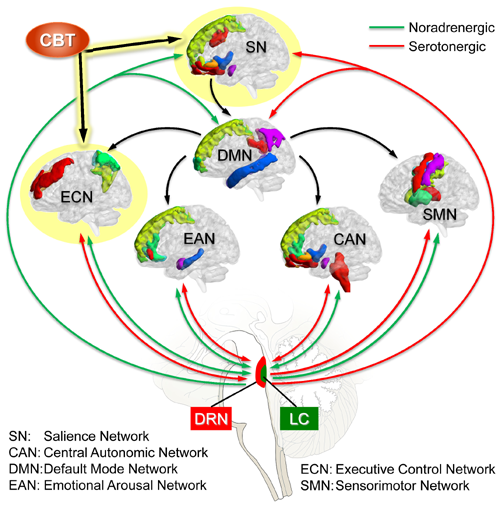
Sex as a Biological Variable (SABV) in clinical and biological responses to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Although behavioral interventions and specifically CBT has been found to be among the most effective interventions for improvement of IBS symptoms, there has been limited attempts to test how BGM alterations in IBS are impacted by CBT and if sex differences exist. We have tested the effect of CBT in a preliminary study which showed that that CBT responders were predicted by a specific microbiota profile at baseline and that this microbiota profile changed with CBT and was associated with a significant reduction in connectivity between brainstem and relevant brain networks, and between emotional arousal, salience and sensorimotor networks. This study will study sex differences in CBT’s effect on BGM interactions in IBS.
Studies suggests a prominent role of the LC (and its central ascending noradrenergic projections) and of the DRN (and its ascending serotonergic projections) in the pathophysiology of increased emotional arousal and stress responsiveness in IBS characterized by increased emotional arousal which have a greater prevalence in women (see Figure).
General Hypotheses
- Positive clinical response to an IBS-targeted CBT is associated with alterations in specific brain and brainstem regions related to sensory processing and perception
- CBT-induced brain changes are associated with alterations in neuroactive gut microbial metabolites suggesting a possible causal relationship
- There are sex differences in these BGM interactions that can lead to differential treatment outcomes between female and male patients.
Specific Aims
Aim A. Identify sex differences in the impact of CBT on the connectivity between brainstem nuclei and brain networks, and between these networks at rest and after provocation.
Aim B. Identify sex differences in the impact of CBT on gut microbiome parameters
Aim C. Identify clinical, brain and gut microbiome predictors of CBT outcomes
People
Project Leads: Emeran Mayer, MD (Co-Lead) and Bruce Naliboff, PhD (Co-Lead)

Emeran A. Mayer, MD
Director, UCLA G. Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience; Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Emeran Mayer is the director of the G Oppenheimer Center for the Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience (CNSR) at UCLA and co-director of the P30 funded CURE Digestive Diseases Research Center at UCLA. The CNSR is a NIH-funded, interdisciplinary and translational research center focused on brain gut microbiome interactions in 4 areas: Functional GI Disorders, Inflammatory Bowel Disorders, Ingestive Behavior/Eating Disorders, Chronic Visceral Pain Disorders. Within the CNSR, he has been the PI of a P50 SCOR grant from ORWH/NIDDK on sex-related differences in brain gut interactions with an emphasis on the effects of early adverse life effects on adult stress responsiveness and related brain circuits for the past 15 years. This grant has been successfully renewed over a total of three 5 year funding cycles under hisleadership. He is also the Co-PI of a UO1 grant focused on studying mechanisms of chronic pelvic pain (MAPP), now in its third 5 year funding cycle, and he leads the neuroimaging efforts within the consortium. Under his leadership, CNSR investigators have done pioneering work in applying psychophysiological and advanced brain imaging techniques to study the response of the brain to visceral stimuli in rodent models and human subjects with persistent visceral pain disorders, including IBS, IBD, IC/PBS and vulvodynia, to identify sex related differences in these brain responses, and to evaluate the effectiveness of pharmacologic and mind-based (including cognitive behavioral therapy) therapeutic approaches to some of these disorders. During the last 5 years, they have expanded their research efforts into the role of the gut microbiome in bidirectional brain gut interactions. They have pursued studies looking at the effect of altered autonomic nervous system output to the gut in altering gut microbial composition and function, and have been testing the hypothesis that gut microbial metabolites and inflammatory mediators in vulnerable patients can lead to neuroplastic changes in the central nervous system manifesting in persistent visceral hypersensitivity, cognitive decline and symptoms of autism spectrum disorders.
Publications:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/myncbi/emeran.mayer.1/bibliograpahy/40552943/public

Bruce Naliboff, PhD
Director, Pain Research Program, UCLA Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress; Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
My research has focused on psychological and psychophysiological mechanisms of stress and pain, including sex differences, utilizing a variety of methodologies and with particular emphasis on visceral pain disorders such as IBS. The development and assessment of nonpharmacological treatments targeted at chronic pain has also been a significant focus of my research. These include cognitive behavioral therapies as well as alternative medicine treatments of yoga and meditation. An important theme of this research is the use of both psychological and physiological measures (including autonomic assessment and brain imaging) to better understand the mechanism of change from non-pharmacological interventions and use of this information to guide better targeting of treatments to specific problems and individual phenotypes. My role Project Co-Leader for Project 3 in the current application involves working on the overall design, assessment protocols and application of the CBT treatment to interventional phenotyping. I have a long and close collaboration with Dr. Mayer, Dr. Chang and the other Investigators who will have my extensive background in behavioral, perceptual, psychophysiological and intervention research applied to chronic pain at their disposal throughout the study.
Publications
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/myncbi/bruce.naliboff.1/bibliograpahy/44607532/public/
Studies
Coming soon
